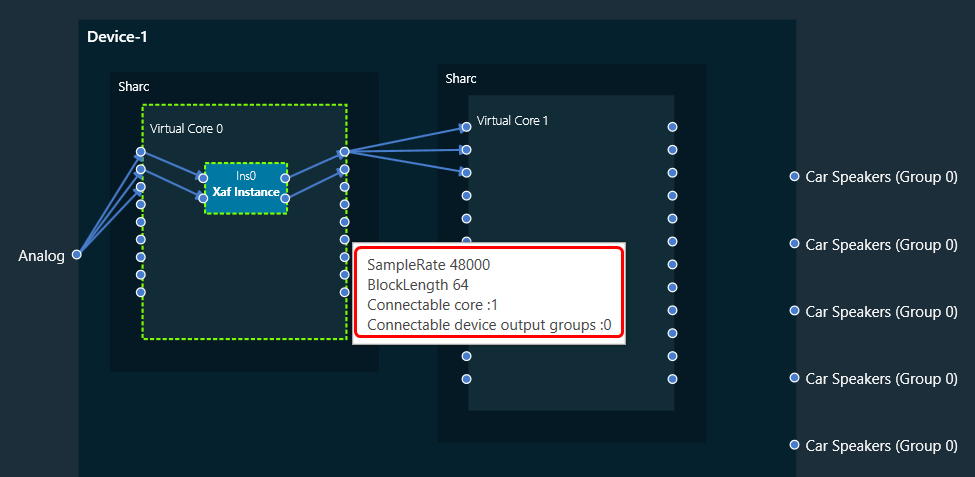
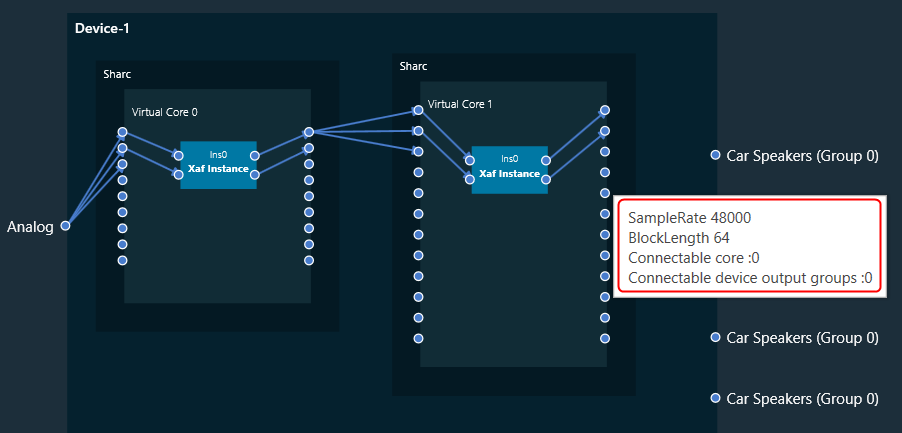
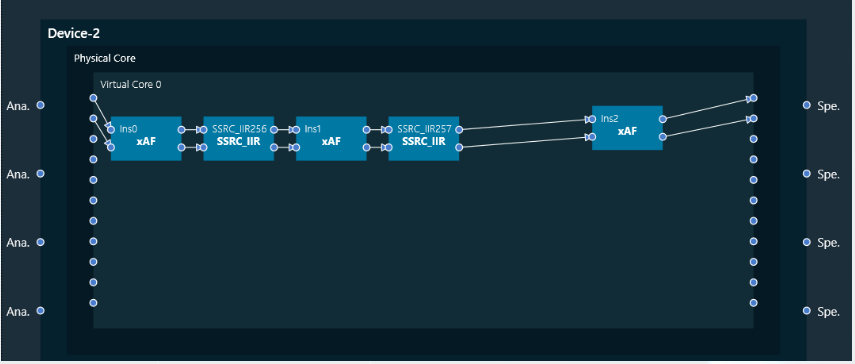
The Real Time Analyzer (RTA) is a tool used to measure and analyses sound waves in real-time. RTA typically consists of several features, that are grouped into various categories to help you navigate and utilize the tool effectively.
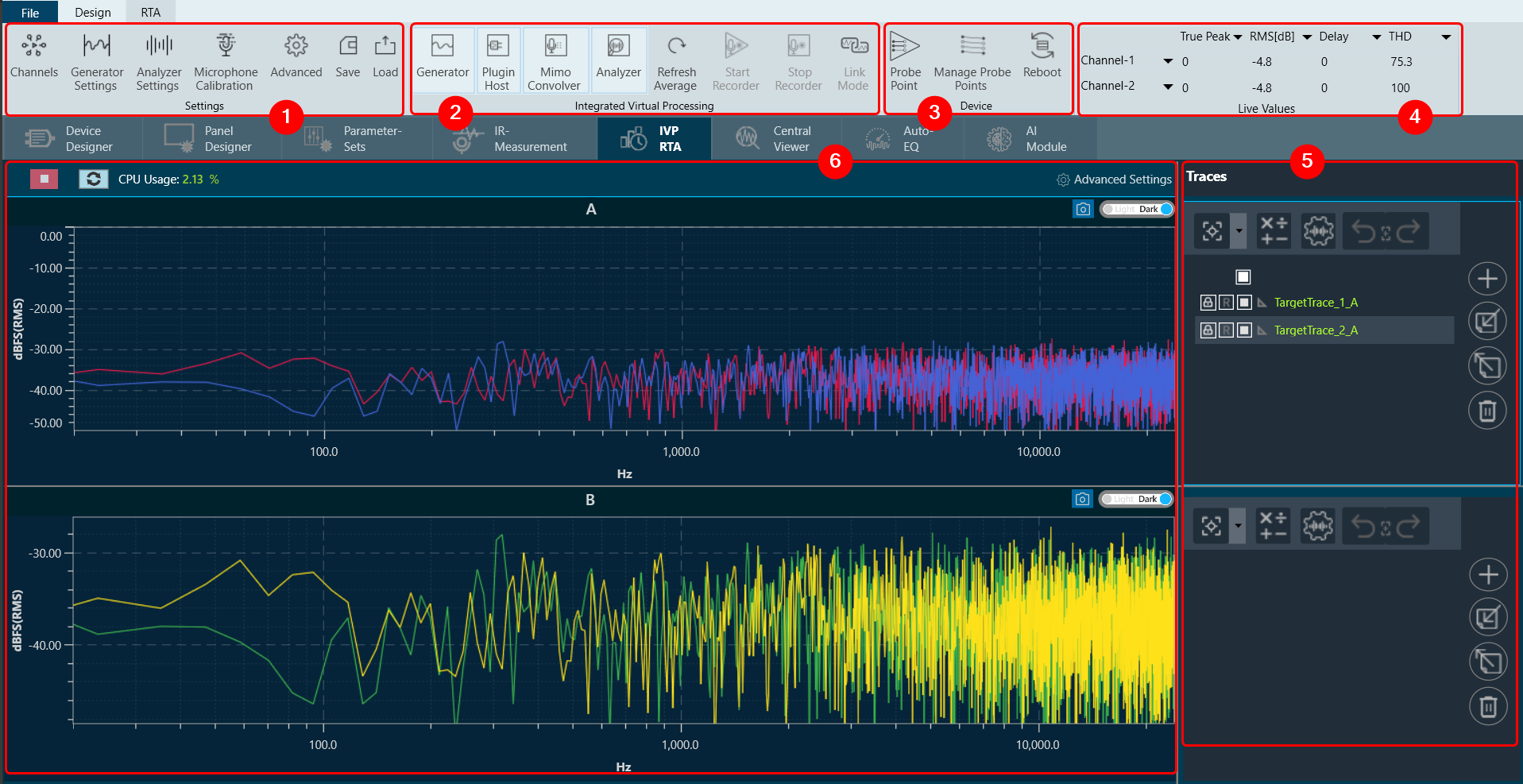
Following are components of Real Time Analyzer:
1. Settings: In an RTA (Real Time Analyzer) window, you can configure various types of settings, that includes:
2. Integrated Virtual Processing: In the Integrated Virtual Processing group of an RTA (Real Time Analyzer), you can find various types of processing options that allow you to generate and analyze the audio data. For more details refer Integrated Virtual Process.
Below are the processing options included in IVP.
- Plugin Host
- Mimo Convolver
- Analyzer
- Refresh Average
- Start Recorder
- Stop Recorder
- Link Mode
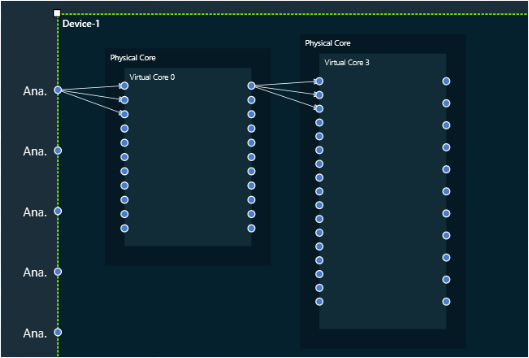
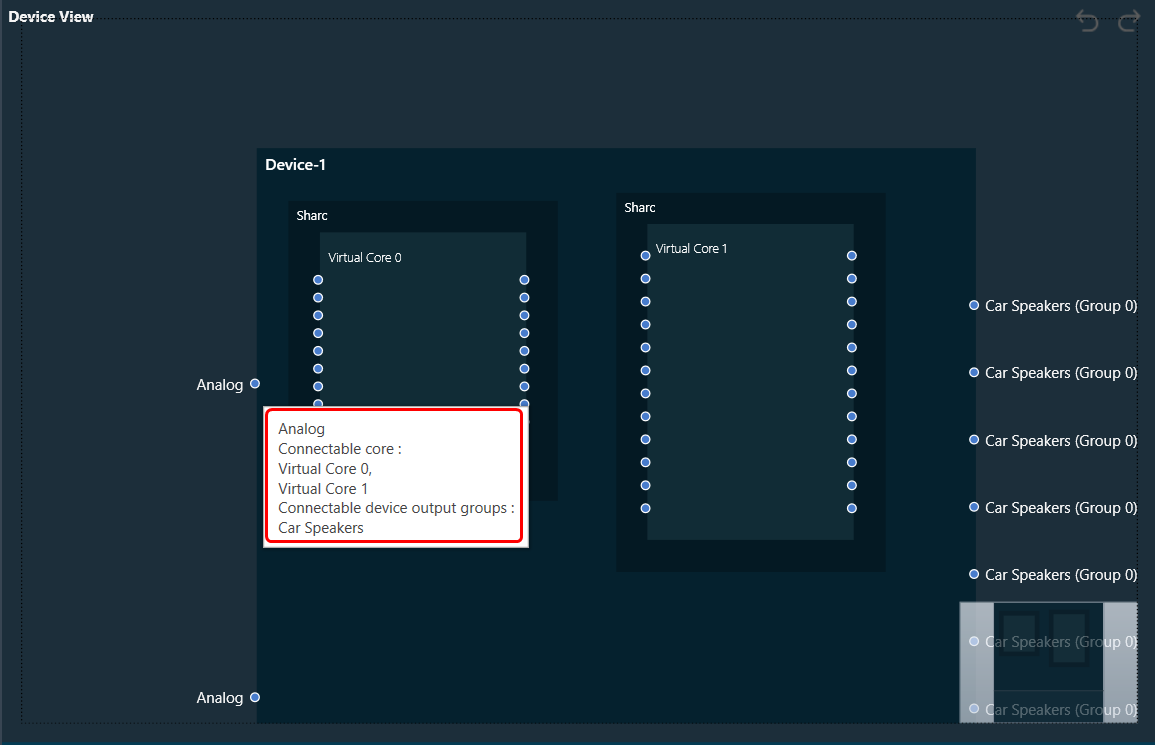
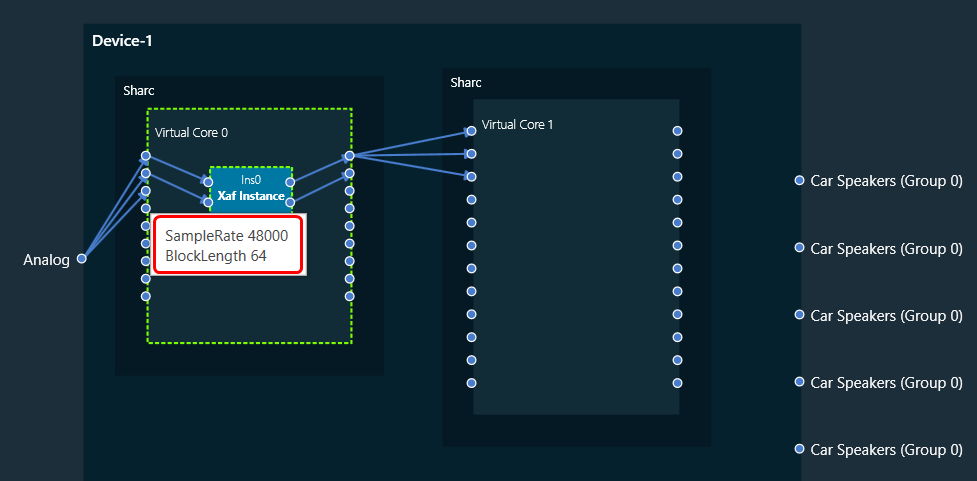
3. Device: This group enables you to manage the probe points of your device. Additionally, it supports the streaming of data from any point in the signal flow back to GTT, allowing for analysis, recording, or reuse of the data within IVP. Below are features included in the group
4. Live Values: In the section, you can easily view the real time values of RMS, THD, Peak, Peak-Frequency, and THD+N for selected two channels. For more details refer to Real Time Data view.
5. Traces: The trace in RTA is a captured measurement curve. Traces provide the ability to plot multiple measurement curves captured at different times on the same graph, allowing for easy comparison of measurements. For more details refer to Traces.
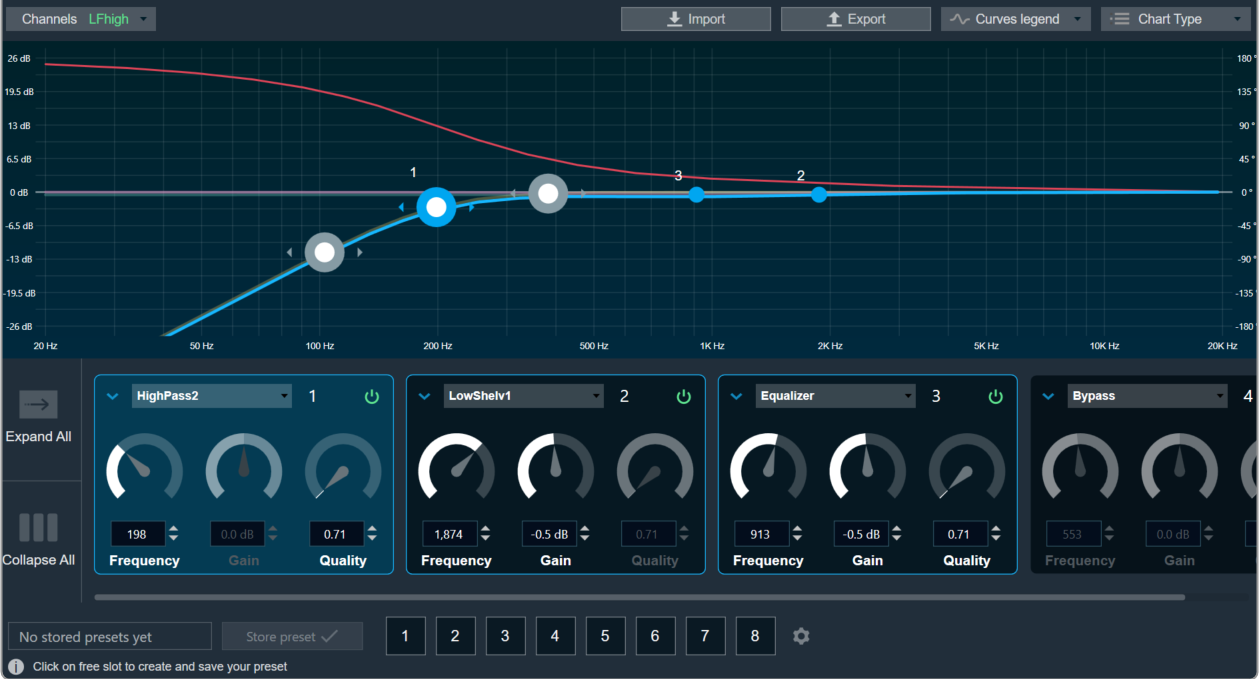
6. Graph Analyzer: This section shows a graph of the audio signal, which enables the analysis of the spectrum of the audio signal. For more details refer to Graph Settings and Measurement.