Audio Object Developer Guide
- Purpose of this Document
- Overview
- Audio Object Configuration
- Basic Features and APIs
- Advanced Features and APIs
- Audio object Example Object
- General Guidelines
- Adding External AO into AudioworX Package
- Building External Audio Object
Starter Kit Developer Guide
- Overview
- Assembling and Configuring Starter Kit Components
- Setting Up the Developer Environment
- SKUtility Developer Options
- Build AWX External Object
- Running Debug Session
xAF Integration User Guide
Troubleshooting
3.1.Design Time Configuration
- Audio Object Developer Guide
- Design Time Configuration
The steps below are the minimum required to setup the configuration of an audio object that can be designed from SFD. The base class (CAudioObject) methods must be overridden and the framework will use these overridden methods to provide structures to inform SFD of your object’s settings. These methods are provided to GTT/SFD via a DLL interface.
The designing of the audio object, start with configuring object descriptions.
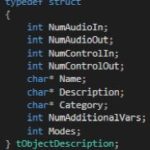
The object description describes the default configuration of the object, when the object is dragged into signal flow designer view in GTT. Default configuration of the object will be Name, Description and Category of the object. Additionally, supported operating Modes and the objects required Additional configuration variables.
The table provide details of description of variables :
|
Member
|
Description
|
|
NumAudioIn
|
This is the default number of audio inputs. It can be overridden as the object is configured.
|
|
NumAudioOut
|
This is the default number of audio outputs. It can be overridden as the object is configured.
|
|
NumControlIn
|
This is the default value, which can be overridden during the design of the audio object and refers to the number of input control signals an object receives.
|
|
NumControlOut
|
Same as NumControlIn but for output.
|
|
Name
|
This is a string with the name of the object.
|
|
Description
|
This describes what the audio object does.
|
|
Category
|
There are various categories in the SFD. This will sort the audio object under that category. For example, the category for a biquad object is “filter”
|
|
NumAdditionalVars
|
This is the number of additional variables an object needs for design configuration purposes. The minimum is 0
|
|
Mode
|
This is the number of modes the object supports. The minimum is 1.
|
The object developer needs to set m_Descriptions in the header file:
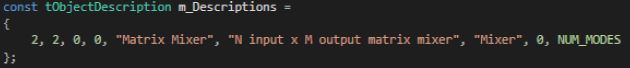
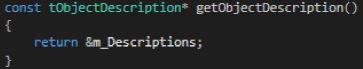
Once the object description is set, developers need to override the virtual getObjectDescription method inherited from the base class CAudioObject:
Once the object’s overall description is provided, a mode description has to be provided for every “Mode” supported by the object. This number is specified in the section above.
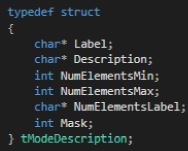
The table below provides a description of the variables required to describe each mode:
|
Member
|
Description
|
|
Label
|
The label of the mode described in the subsequent fields.
|
|
Description
|
Description of what this mode does.
|
|
NumElementsMin
|
The minimum number of elements permitted.
|
|
NumElementsMax
|
The maximum number of elements permitted.
|
|
NumElementsLabel
|
The label for the number of elements. For example, the number of elements in the Parameter Biquad block represents the number of Biquad filters within the Biquad block. This field is populated with ’Number of Biquads‘ for the Biquad block.
|
|
Mask
|
Four bits are used to indicate to GTT if it is possible to configure the audio channels and the number of elements (one for configurable):
|
The basic configuration information is written to the m_Descriptions variable in the audio object header file. The tObjectDescription structure displays all the variables necessary for configuration that are not dependent on the mode of the object.
For a mode dependent description, the tModeDescription needs to be provided. The example below describes and object that has 2 modes.
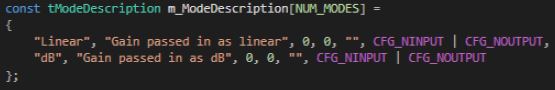
Once the mode description(s) is set, developers need to override the virtual getModeDescription method inherited from the base class CAudioObject.

Additionally, developers must implement a function for each audio object that describes the audio and control I/O, based on what they configured in the design tool. This function interacts with the object through the dll described above. The code below shows an example of this function implemented for the merger object that always has zero controls and only number of audio inputs is configurable. The number of outputs is dictated by the number of audio inputs as seen below.
xAF_Error CMergerToolbox::getObjectIo(ioObjectConfigOutput* configOut)
{
configOut->numAudioOut = m_NumAudioIn + 1;
configOut->numControlIn = 0;
configOut->numControlOut = 0;
return xAF_SUCCESS;
}
This method may rely on the following member variables depending on the object mask.
- m_NumAudioIn
- m_NumAudioOut
- m_NumElements
- m_Mode
- m_AdditionalSFDConfig
configOut is made up of the settings returned by the getObjectIo() function and is composed of:
- numAudioInputs
- numAudioOutputs
- numControlIn
- numControlOut