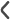Global Tuning Tool
- About Global Tuning Tool
- Workspace Overview
-
Configurations
- Configure State Variable
- Configure Default Control-Ids
- Configure Preset Controller
- Link Window
- Configure Controller
- Launch MIPS Profiling
- Launch Memory Profiling
- Editing Memory Latency
- Configure Streaming and Polling
- Configure File controller
- Configure Control IDS
- Custom Device Usage
- Multi-xAF Library Support
- Configure External Endpoints
- Operations
Signal Flow Designer
- Overview Of Signal Flow Designer
- Components of Signal Flow Designer
- Operations in Signal Flow Designer
- Create a Signal Flow
- Tune a Signal Flow
- Native Panels
- Additional Audio Parameters
- Harman Audio Library Service
- Multiple Framework Instances Support
- Feedback loop in Signal Flow
- Compound Audio Object
Audio Object Description
- Audio Object Description Overview
- Audio Object General Information
- Interface Objects
- Basic Objects
- Control Objects
- Routing Objects
- Source Objects
- Mixer Objects
- Dynamic Object
- Filter Objects
- Core Objects Toolbox
Panel Designer
- Panel Designer Overview
- Panel Designer Components
- Create a Custom Panel in GTT
- Switch between Multiple Parameter Sets
Parameter Set
Real Time Analyzer
- Real Time Analyzer Overview
- Real Time Analyzer Components
- Settings
- Integrated Virtual Process Options
- Probe Point Configuration
- Real Time Data View
- Graph Settings and Measurement
- Traces
- Analysing Audio Signal
Measurement Module 2.0
Central Viewer
Starter Kit Utility Tool
2.2.1.Tools
- Global Tuning Tool
- Tools
The Tools group allows you to monitor all services running on GTT, view the event and xTP logs, and perform the sound card configuration.
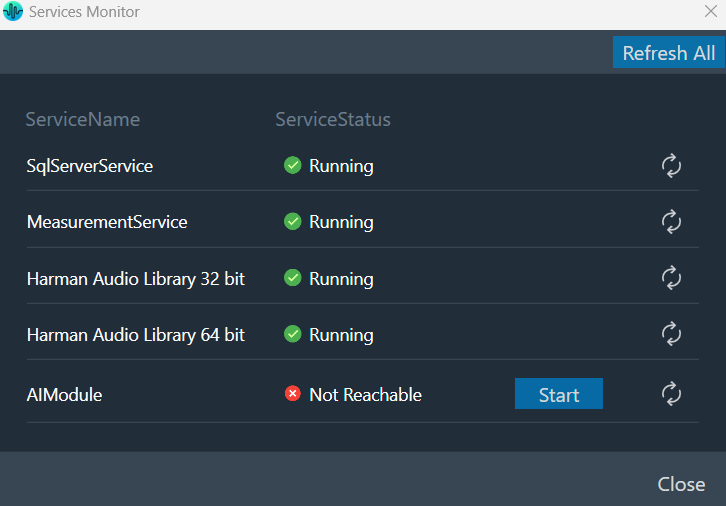
Global Tuning Tool provides a comprehensive set of tools for monitoring the following services:
- SQL Server Service
- Measurement Service
- Harman Audio Library 32
- Harman Audio Library 64
- AI Module
The choice of tool depends on the type of monitoring or tuning to be done and the events to be monitored.
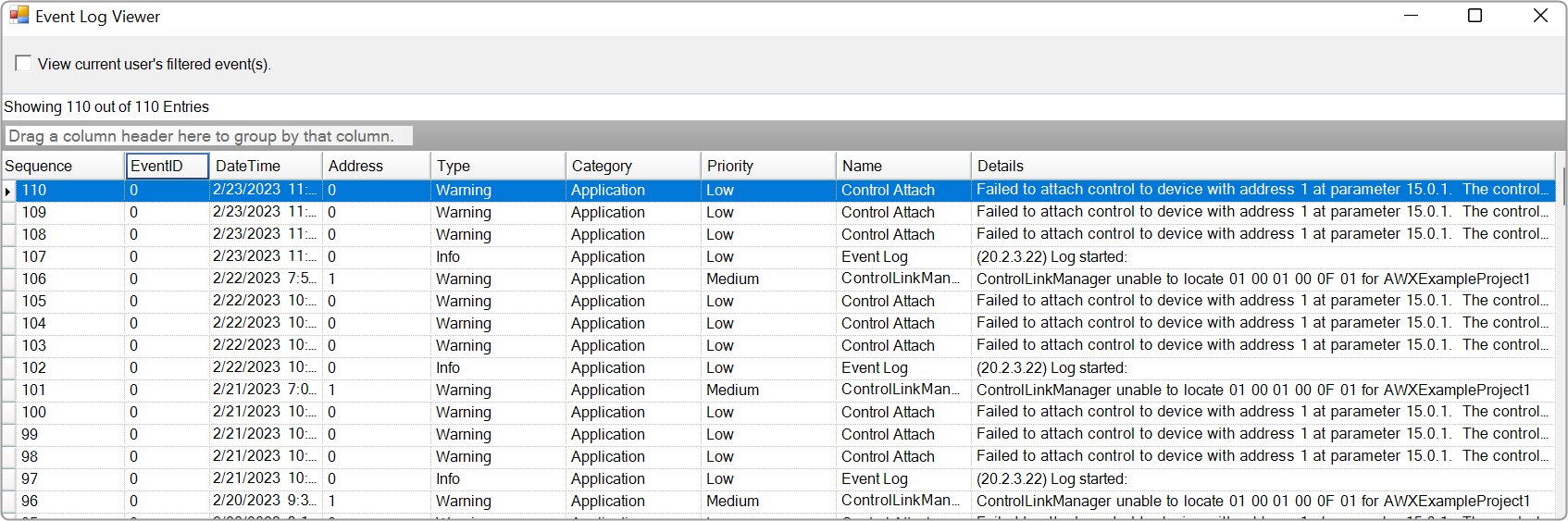
The Event Log window tab shows events that have occurred within the Global Tuning Tool and on connected devices. The log may be utilized by individual devices to perform certain operations. You can also use the logs for troubleshooting.
The Event Log Indicator will notify you in real-time as events occur.
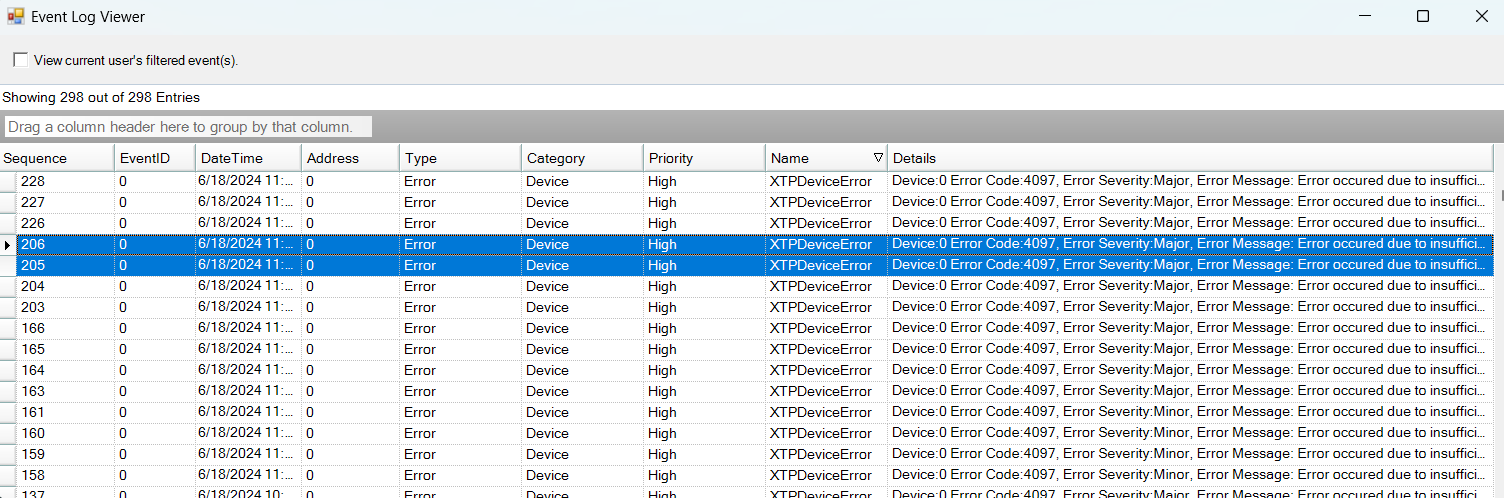
Any error on the device is displayed in GTT in the XTP viewer and Event log.
The xTP-Viewer has two sections:
- Left side section: Display message flow view and show raw data of several messages.
- Right side section: Detailed view of a selected message on the right side (is empty if message interpretation is not implemented up to now for the specific message).
The Sound Card Setting allows you to configure the host API (audio driver), device, sample rate, block length, and the master output for the audio processing. Based on device selection, input and output channels are available for configuration.
Using “Master Output” you can set master and device output modes for speaker configuration in the Measurement Module.
The configured sound card configuration is used throughout the RTA and Measurement Acquisition features.
Before you start the Measurement wizard or set the “Sound In” and “Sound Out” devices in the RTA, make sure you have configured sound card settings like Host API (Driver Protocol), Device, Sample Rate, and Block length of the sound card.
On the “Streams” section list of available channels for input and outputs is displayed. Those can be routed to any physical sound card channels. All devices are available as two-channel devices. The stream area displayed the Channel column, indicating the mapping of Sound In or Sound Out devices to specific channel pairs.
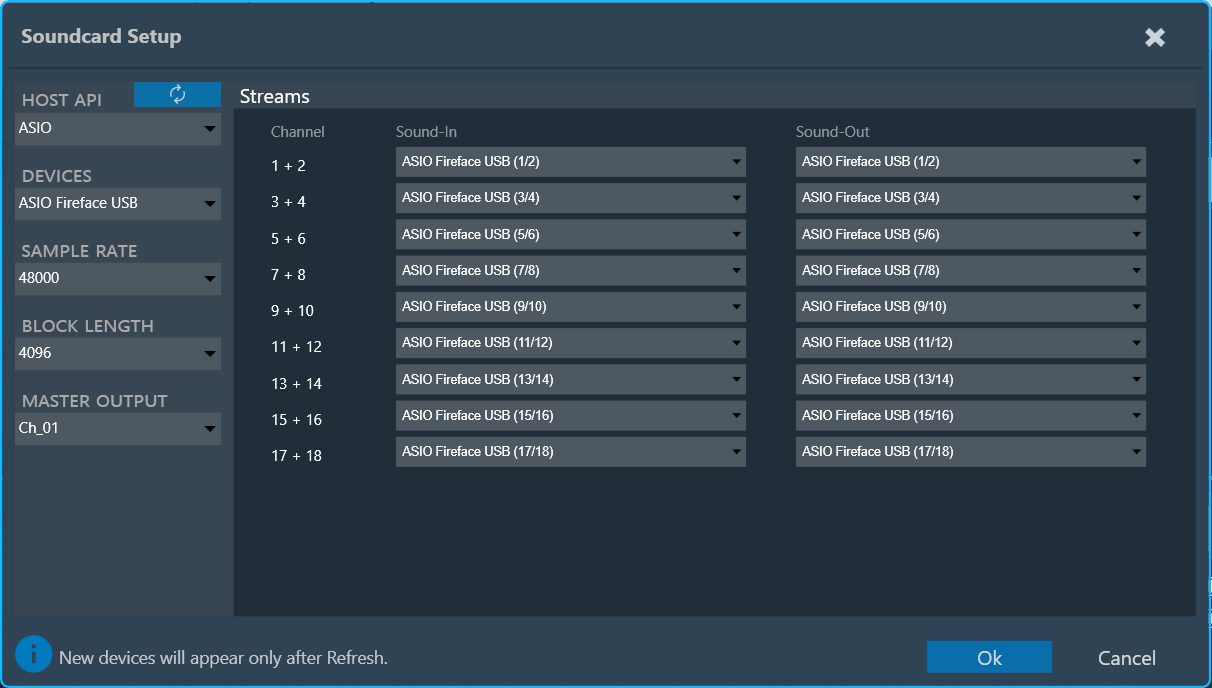
In the example above, the mapping is configured as follows:
- SoundIn1, SoundIn2: Analog (1 + 2)
- SoundIn3, SoundIn4: Analog (3 + 4)
- SoundIn5, SoundIn6: Analog (5 + 6)
- SoundOut1, SoundOut2: Analog (1 + 2)
GTT supports four host APIs: MME, Windows DirectSound, ASIO™, and Windows WASAPI.
| Host API | Description |
| MME | This is the standard Windows audio API. It allows the operation of multiple audio devices at the same time. Sample rates are handled by the operating system. Can be set to any sample rate. If the sample rate of the physical audio device is different, then the OS takes care of the sample rate conversion. This mode is recommended if multiple devices are running at the same time, e.g measuring with a USB microphone while playing back generator signals with an internal sound card. For MME, it’s required to select input and output devices separately, and all selected input and output devices support a maximum of 2 channels.
Recommendation: Keep the block length at the maximum value of 4096 and the sample rate at 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz. |
| ASIO™ | This API is used with multi-channel sound cards. It enables low latencies and ensures that all input and output channels are in sync. Depending on the latency requirements of the audio signal processing provided by a loaded plugin (future feature) the block length can be reduced down to 64 samples. The RTA sample rate setting has to be equal to the audio device driver sample rate. It’s not required to select separate input and output devices for ASIO™. |
| Windows Direct Sound | This Windows API has improved latency compared to MME as it has more precise buffer control. Sample rate mismatches are handled by the operating system, similar to MME. Input and Output devices are to be selected separately, and they support a maximum of 2 channels. |
| Windows WASAPI | Is Microsoft’s most recent API. Latency has improved compared to MME and Direct Sound. This API does not support an output-only selection, as it requires a clock signal from the input. The operating system does not handle sample rate mismatches; instead, the user is responsible for ensuring that the sample rate of the physical device aligns with the RTA sample rate. Input and output devices must be selected separately, and both support a maximum of two channels.
The following are the limitations of Windows WASAPI
|
– It is recommended to use an ASIO™ sound card instead of Windows drivers if possible.
– When using Windows drivers, it is advised to use a block length greater than 1024 in order to avoid the noise distortion effect and high cpu load issues.
– The setting for the sample rate does not change the actual setting in the sound card driver. The alignment of the sample rate setting has to be ensured by the user.
Supported Soundcards
-Fireface® UCXII
– TASCAM® US16-08
– Fireface® UC
– Ultralite® AVB, 18 x 18 USB/AVB Audio Interface (Motu)
– Focusrite® – Scarlett 2i4, 2nd Gen
– Creative Soundblaster® X4
During sound card configuration, channel streams should be automatically assigned with available input and output devices if the user has not already assigned any sound input or output devices to RTA Channel streams.
If the user attempts to unassign all sound card channels, a toast message should be displayed with a message like “You have unassigned all sound card channels. This will disable the internal IVP processing, because no lock master is available. Please assign at least one channel pair to re-enable the processing”.
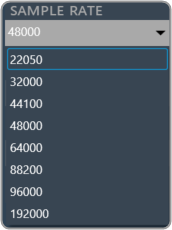
Supported sample rate

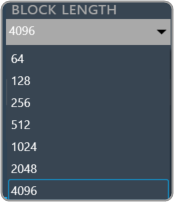
Supported block length

If there are any modifications to the Sample Rate, Block Length, or Host API, it is necessary to reconnect the device Sound card settings impact in RTA
The Microphone Setup allows the calibration of microphones and assigns a mic compensation file for each microphone. The configured values will be applied across the GTT wherever microphones are involved, such as in the RTA and measurement modules. This view can be accessed from the “Microphone Setup” button in the “Design” ribbon tab.
Every microphone element (1 or 6 microphone array) must be calibrated separately. The central element of the calibration menu is the list of microphones contained in the current microphone element.
The list has the following columns:
- Microphone: The number of the microphone within the element.
- Sound-In: The stream channel number is configured with the physical channel of the sound card in the Sound Card Setup view. Duplicate channel assignments to microphones are indicated in orange.
- Previous value: Offset measured during the previous calibration, displayed as a comparison.
- Current value: The offset measured during this calibration.
- Compensation File: This is the File provided by the mic manufacturer, which will be used for magnitude curve correction. The current supported format is a .txt file. The supported file format is attached here: M4261-Microphone-4881.
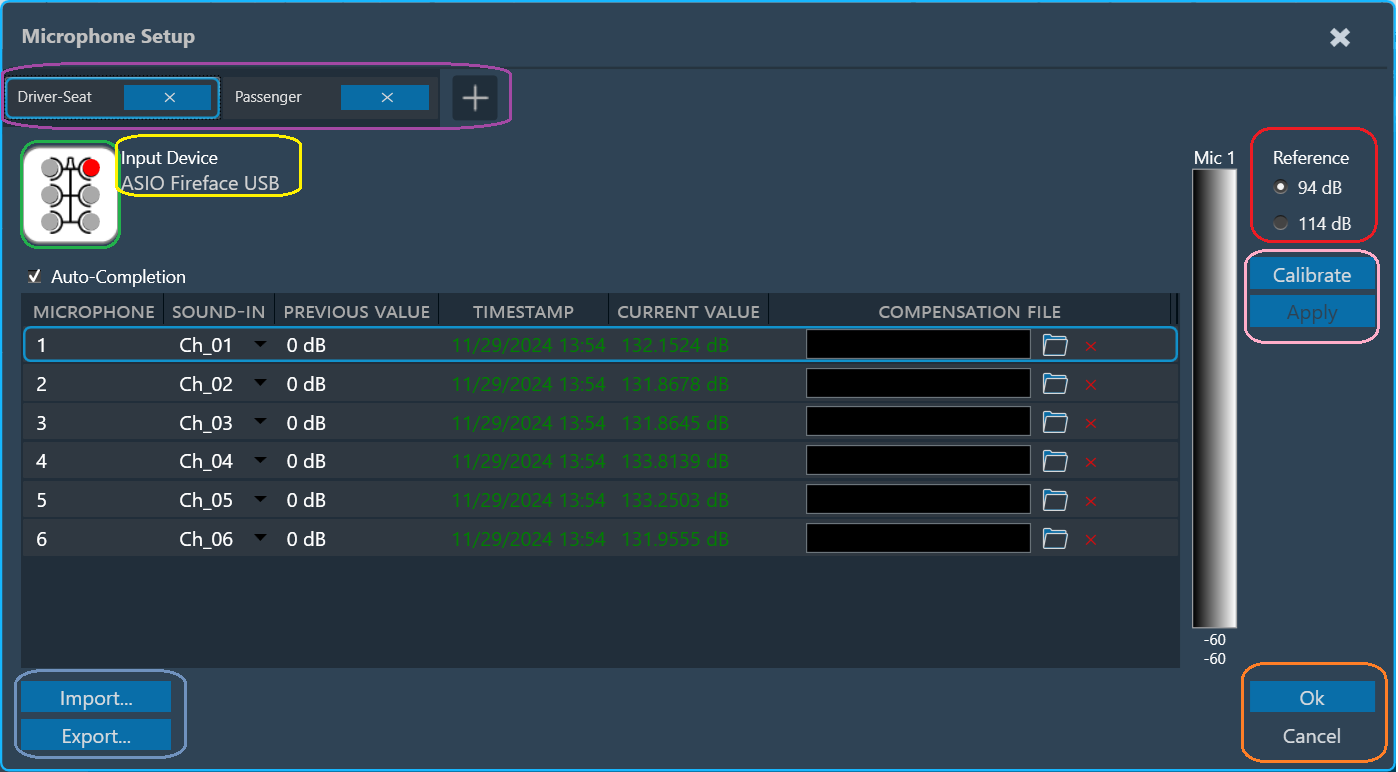
The type of the microphone element and the currently selected microphone within the element are indicated using an icon (green rectangle).
The soundcard and the selected microphone is displayed (yellow rectangle).
The reference sound pressure level of the calibrator can be selected in the upper right (red rectangle).
Multiple microphone carriers can be added or removed (purple rectangle). The currently selected/configurable microphone carrier is highlighted in blue.
To calibrate a microphone:
- Choose the Microphone carrier and select the microphone you want to calibrate.
- Assign the channel number. Auto-completion will assist in assigning available incremented channels.
- Attach the microphone to the designated channel on the calibration device. This will connect the calibrator to the microphone itself.
- Select the appropriate reference sound pressure level (SPL) for your calibration.
- Click on Calibrate. The calibration process should take approximately 2 seconds.
While calibration is running, observe the level meter (indicated as a black rectangle) for activity on the chosen input channel.
The calibration will result in an offset value (displayed in red in the “current value” column). - Click on Apply to accept the value (which will turn the value green) or repeat the calibration process if the value is not satisfactory.
- Click Apply confirms the calibration value, turns it green, and automatically selects the next microphone that needs calibration (if applicable).
Repeat the procedure for all microphones in the array.
Individual microphones can be recalibrated at any time. Once all calibration offsets are applied, the menu can be closed using “Ok”.
When configuring multiple microphone carriers, you can easily switch between them, and any changes you have previously configured will be automatically applied.
For any changes in the mic row, the user must click Apply to save the changes before clicking OK.
Import: The “Import” option allows you to import an existing calibration and compensation file path. This sets the current value for all microphones to the stored offsets. The values must be applied. Settings will be imported to the selected microphone carrier.
Export: Using “Export,” you can export a full set of applied calibrations along with the compensation file path to disk. Settings will be exported from the selected microphone carrier. The exported JSON files will contain the Channel Number, Offset, and mic compensation file of the calibrated microphones.