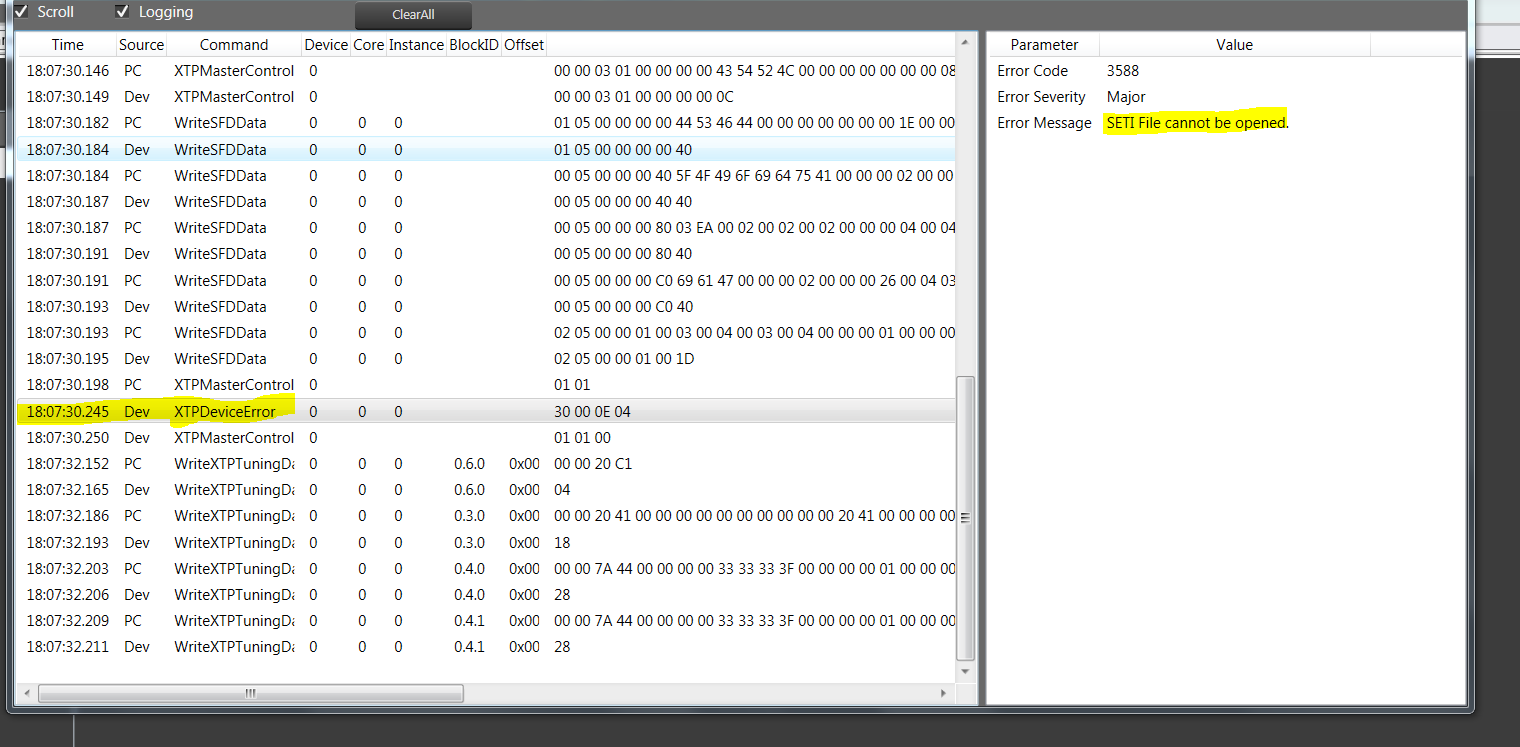
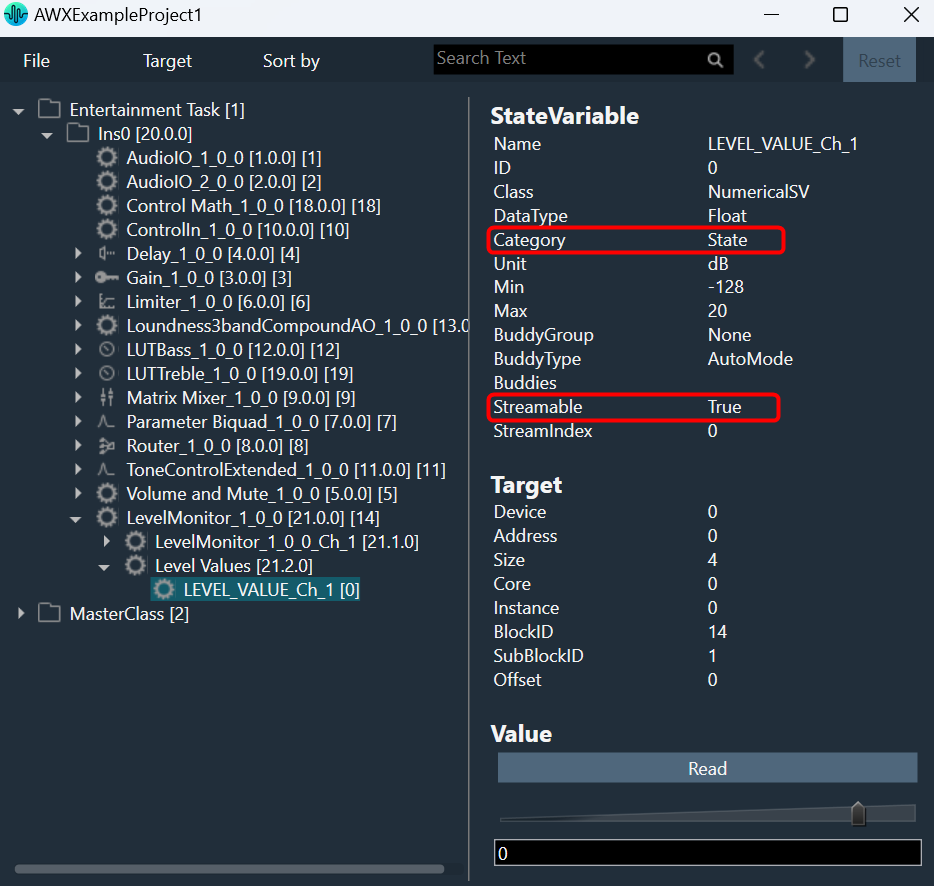
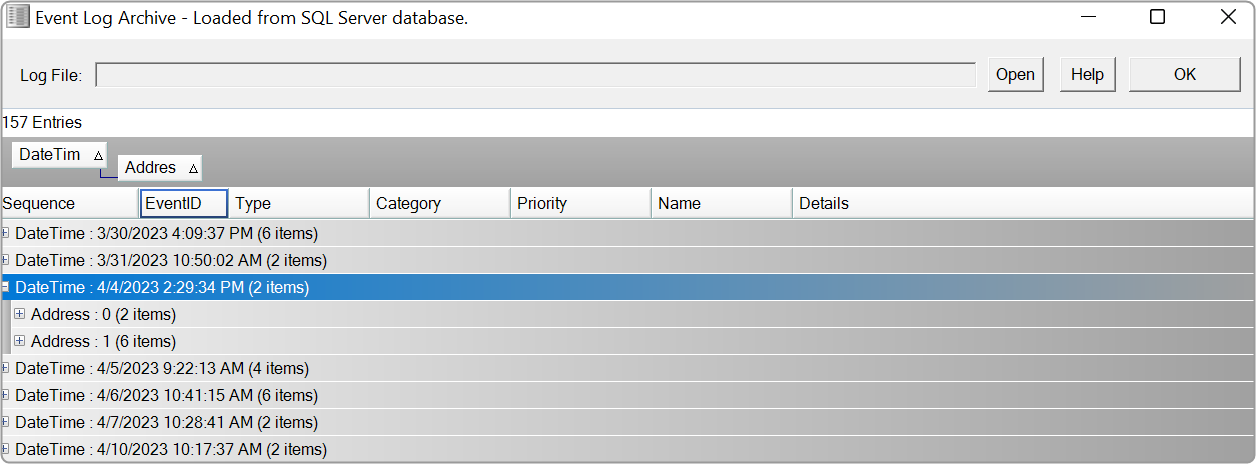
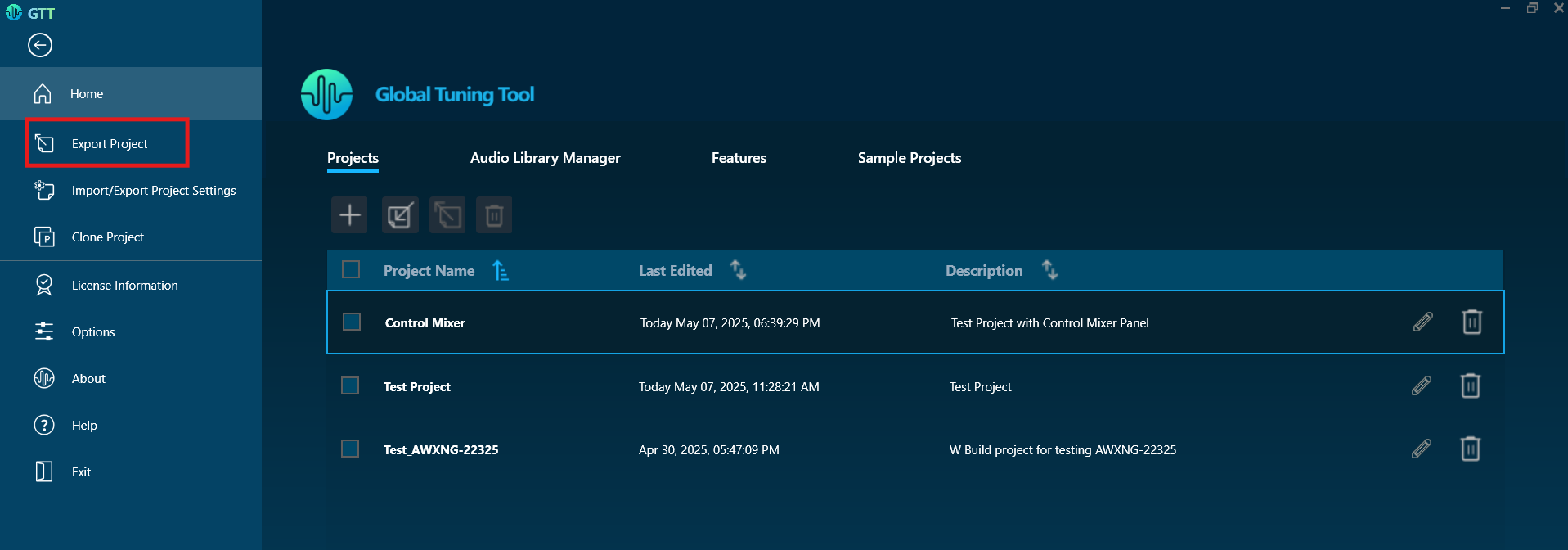
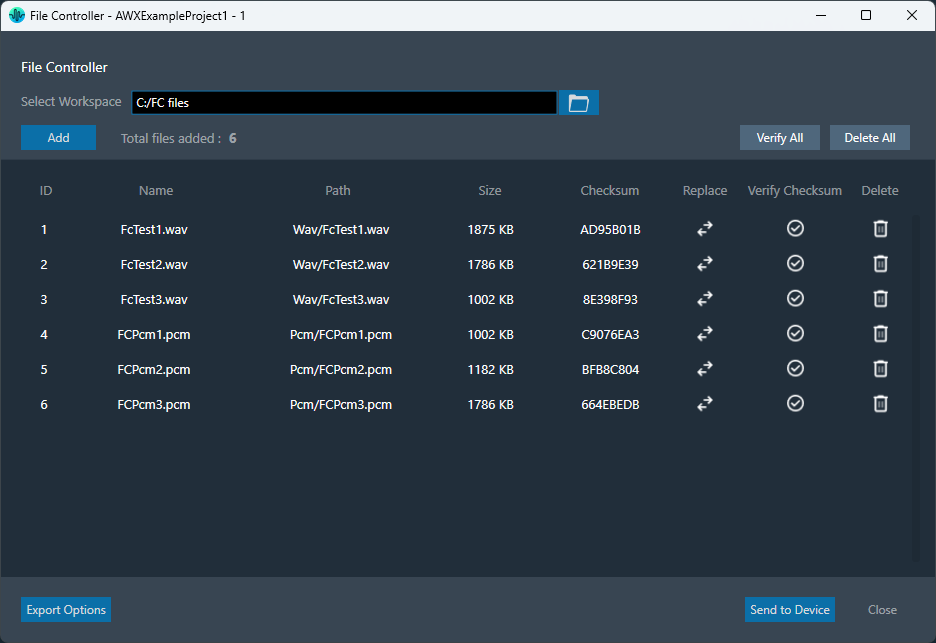
The File Controller allows you to send any type of file(s) from GTT to the device. It does not restrict file type or extension and allows file sizes up to 4GB.
The audio object is responsible for validating that the file being loaded is of the correct type. The file controller does not check the IDs used in audio objects.
Developers and system designers must verify the correct file type when using the file controller. For example, a configuration file should not be loaded into a file player, or a WAV file should not be used as an audio object configuration.
The audio object will return an error state if any invalid file type is detected, and this error must be handled appropriately.
The following are the options available in the file controller.
- Select Workspace
- Add Files
- Delete File
- Replace File
- Send to Device
- Verify Checksum
- Export Options
- Export and Import File Controller Data
The file controller feature is available from W release onwards.
The Select Workspace option allows you to browse and select a workspace or root folder from the local directory. Once the folder is selected, you can add the respective audio files.
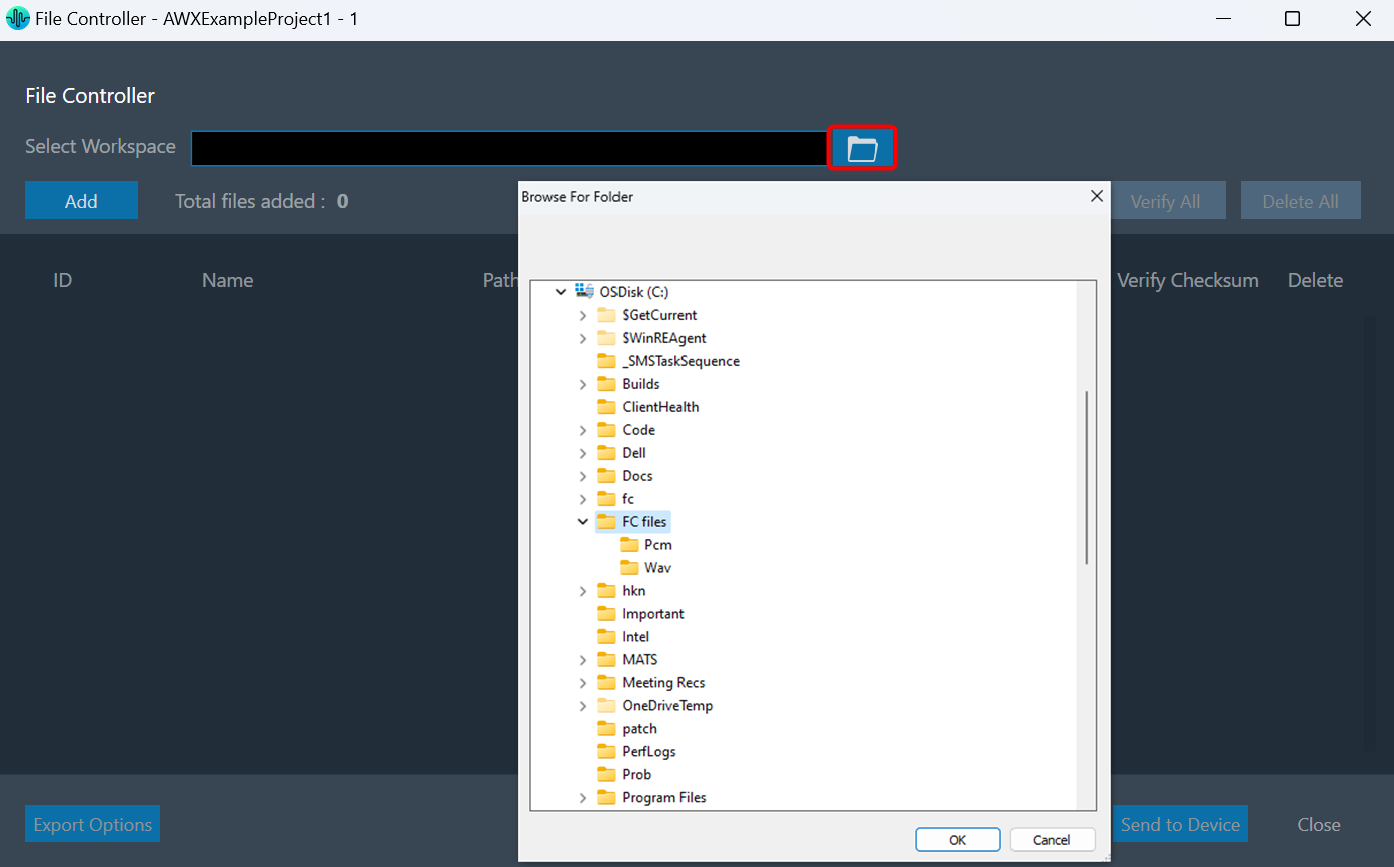
Also, you can copy and paste the path of your workspace folder in the “Workspace” field.
Once the workspace folder is selected, click on the “Add” to launch file browser. You can navigate to the respective folder and add audio files (.pcm/.wav) in file controller from the workspace folder.
The file browser will open the workspace folder by default.
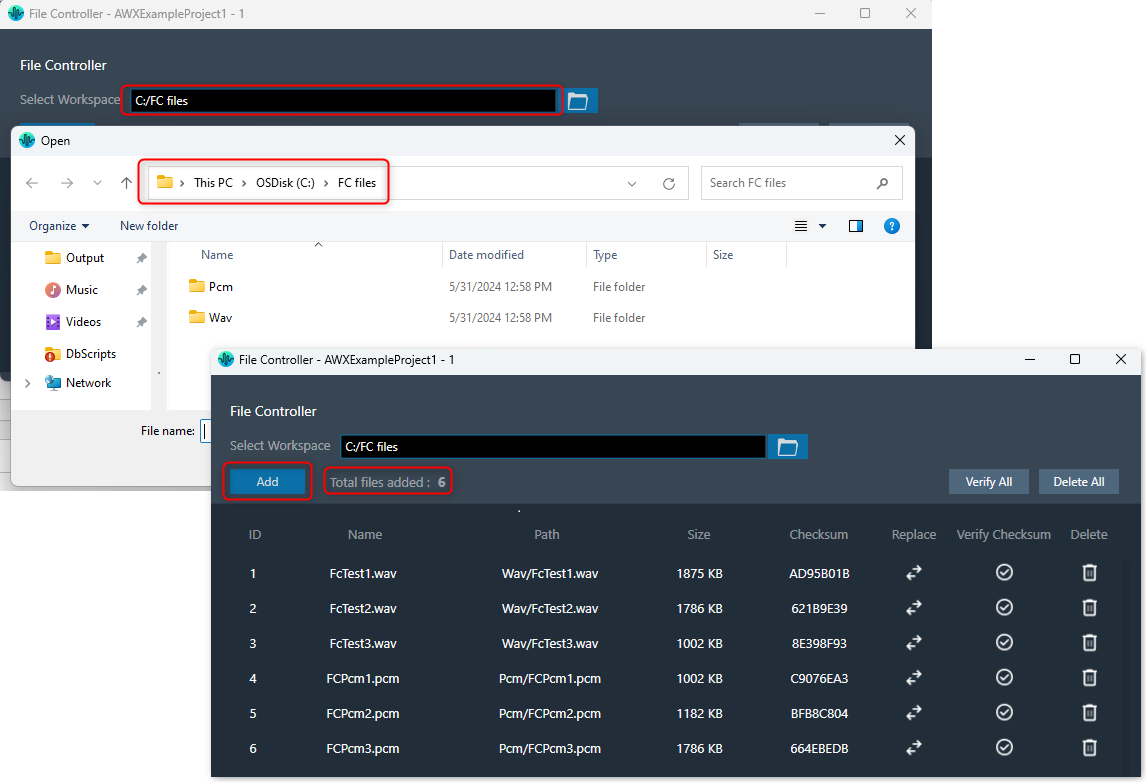
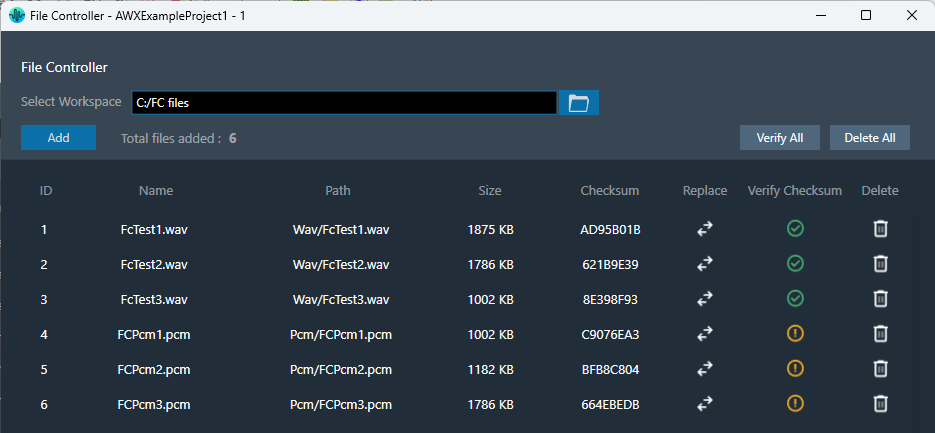
After adding the files, the following details of the files will be displayed in the file controller.
- File ID: This ID is generated from GTT; its range is from 1 to 254.
- File Name: If the file name is exceeding length of 15 characters (including file extension), GTT will trim it to 15 characters.
- Path: Relative path of file, based on the workspace folder selected.
- Size: Size of the file in KB. If the file size is less than 1KB, the size will be displayed in bytes.
- Checksum: Checksum calculated using file content.
In case if you add any file from a non-workspace folder, the following prompt will appear.
- Copy: To create a duplicate copy of the file within your workspace folder.
- Move: To relocate the selected file to your workspace folder, removing it from its original location.
- Cancel: To stop the ongoing operation.
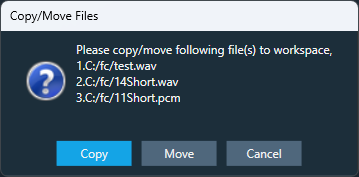
This facilitates the sharing of project files and files added to the file controller by ensuring that all files added to the file controller are present in the workspace folder.
The number of files added will be displayed in the File Controller.
A maximum of 254 files can be added in the file controller.
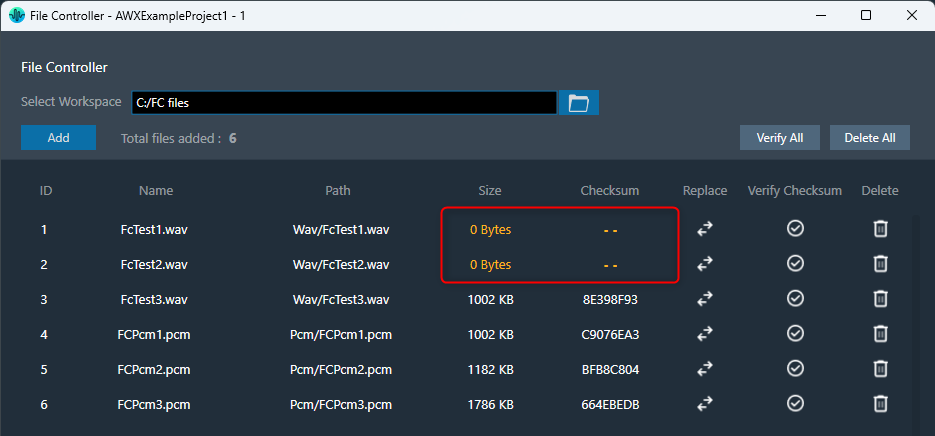
Once after adding files to the file controller, on relaunching the file controller, if any file is not found to load, the error is indicated by showing “0 Bytes” size and invalid checksum as below,
The file controller offers two ways to manage your files:
- Click “Delete All” to remove all files at once.
- Use the “Delete” button for each file to remove them individually.
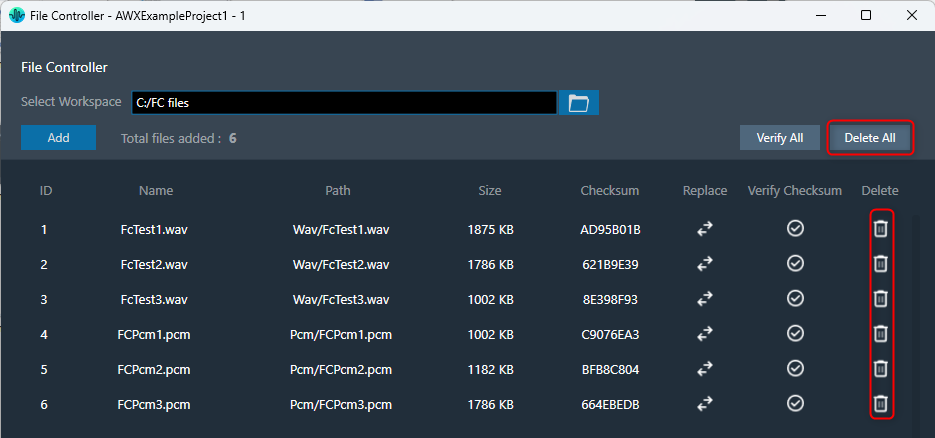
The delete operation will delete the file entry from the file controller, not the file from the file system.
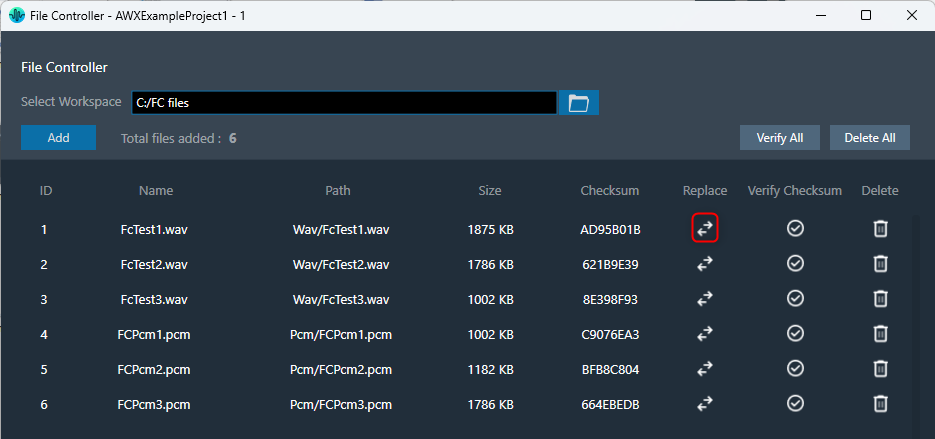
You can replace file in the file controller. Click on the “Replace” button, this will open the file browser, allowing you to select the new file you wish to use.
Also, allows you to reuse the file ID for different files easily.
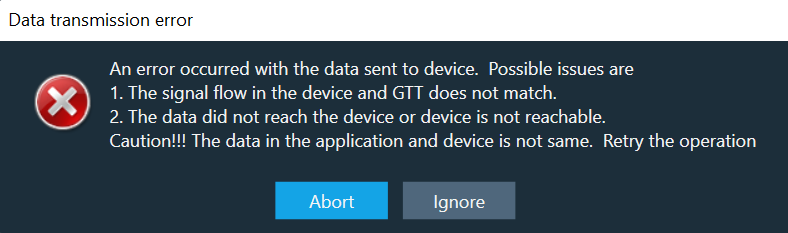
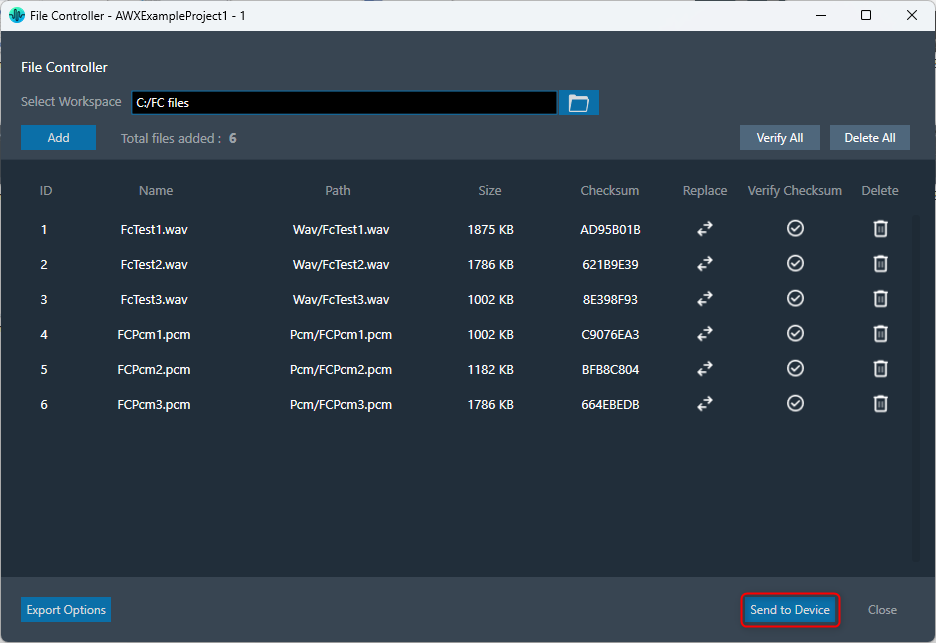
The “Send to Device” allows sending the loaded files in the file controller to the device.
While sending files to device, the file map will be sent to device first. It contains metadata (number of files and sizes) about the files being sent.
If it fails to send the file map, the files will not be transferred to the device.
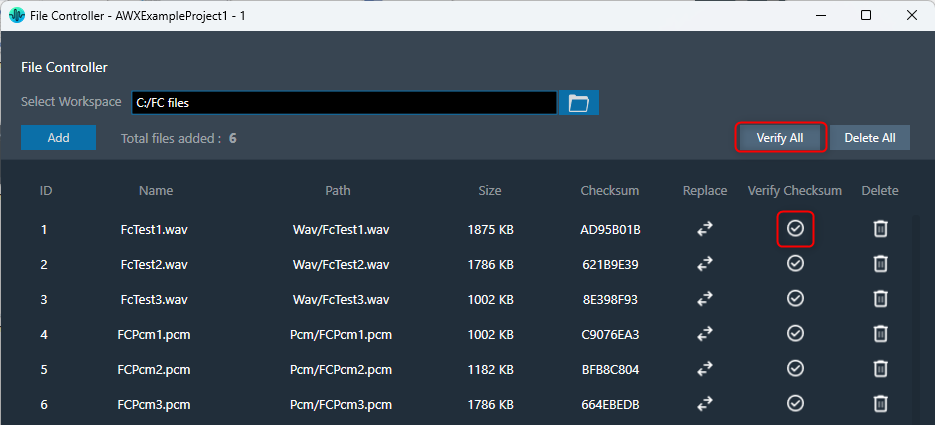
The “Verify Checksum” feature helps ensure you’re working with the correct files. The Verify Checksum option uses the file content checksum to confirm that a file with the same file ID is present on the device.
Use the “Verify All” button to check all files at once, or the individual “Verify” button in each row for specific files.
| Indicates the default state is “Not Verified”. | |
| Indicates when the file is found on a device with the same file ID. Also, when the file is sent to the device successfully. |
|
| Indicates when the file is not found on the device with the same file ID. |
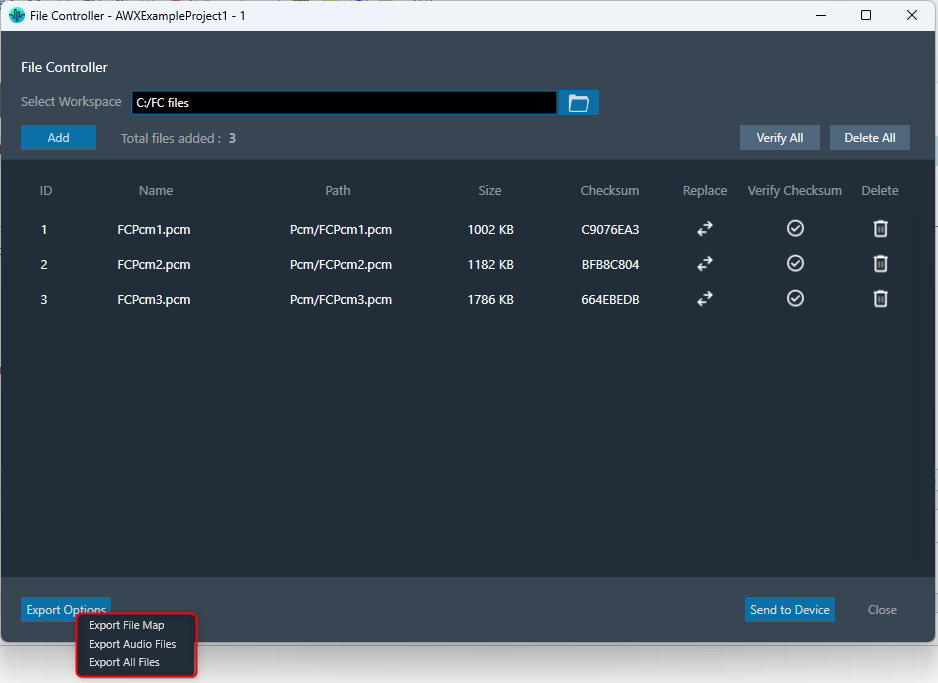
To export files from the file controller, the following options are available.
- Export File Map
- Export Audio Files
- Export All Files
These options will be displayed on clicking the “Export Options” button.
Upon selecting any of these options, a folder browser will open, allowing you to select the destination folder.
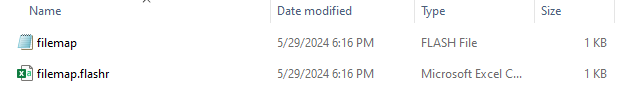
- Export File Map: This option is to export the file map and human-readable file map.
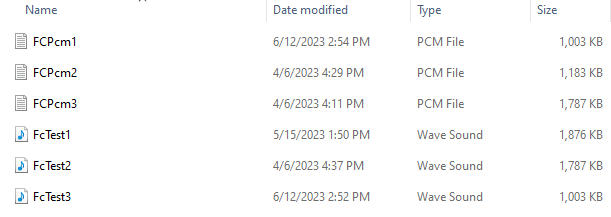
- Export Audio Files: This option is to export audio files added in the file controller.
- Export All Files: This option is to export all files, including the file map and human-readable file map.
Export and Import File Controller Data
The selected workspace and metadata of loaded files in file controller can be exported through project file (.gttd). This metadata includes file ID, name and relative path of file. After importing the gttd file with file controller data, if the workspace folder is not found, files will be displayed with “0 bytes” Size and invalid checksum as shown below.
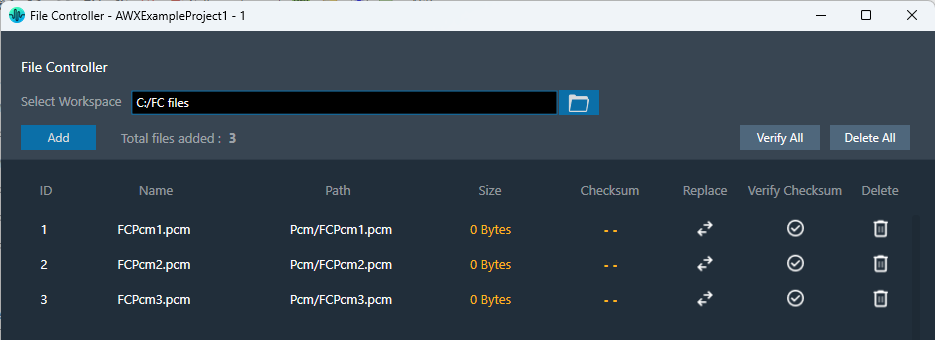
You can select workspace folder with same sub folder structure to automatically reload files loaded in file controller. The files should be present in same hierarchy and name.