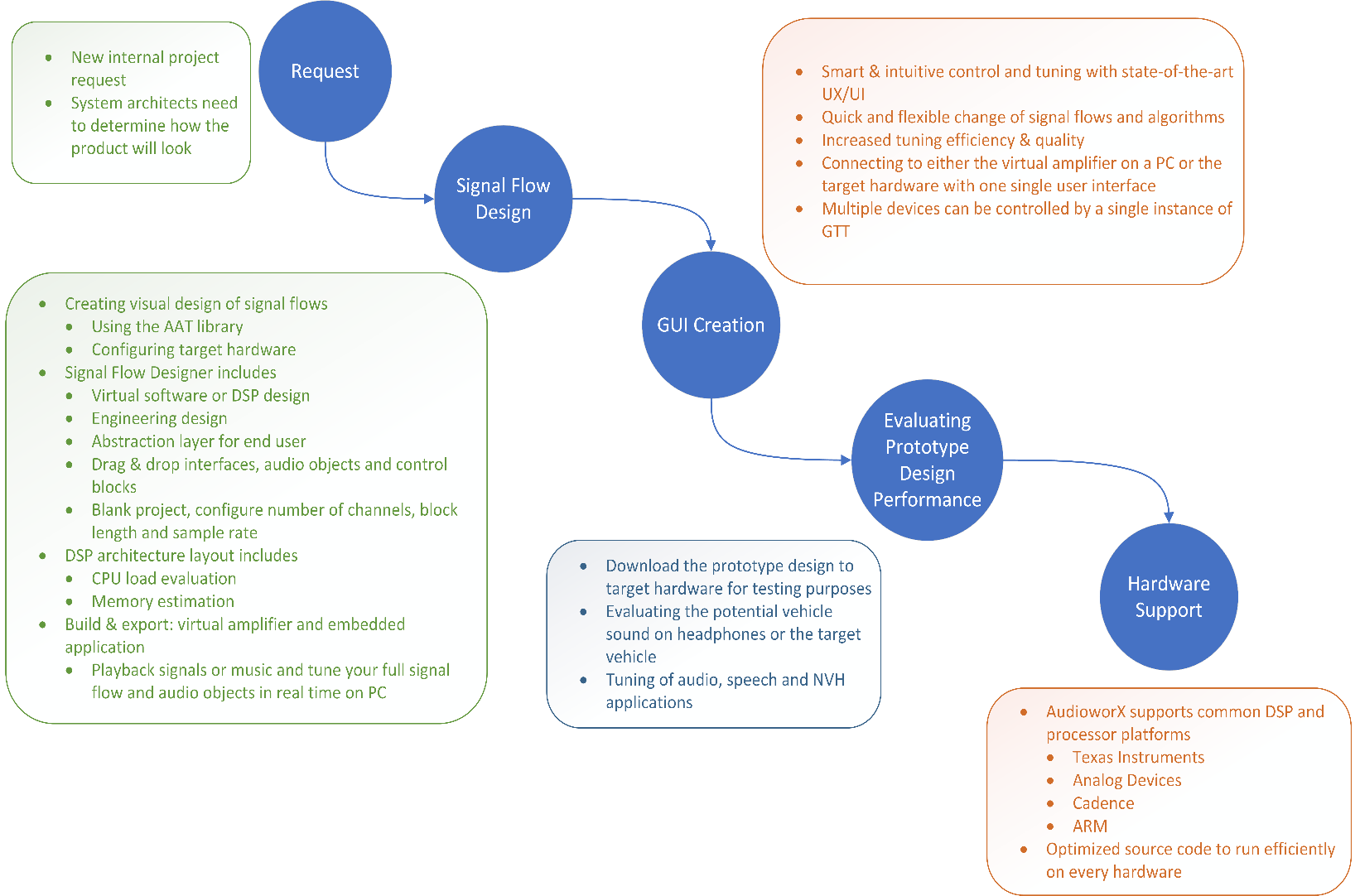
GTT allows external tools to interact with devices. The tuning of 3rd party audio objects can be done directly in GTT, or it can also be done from an external tool.
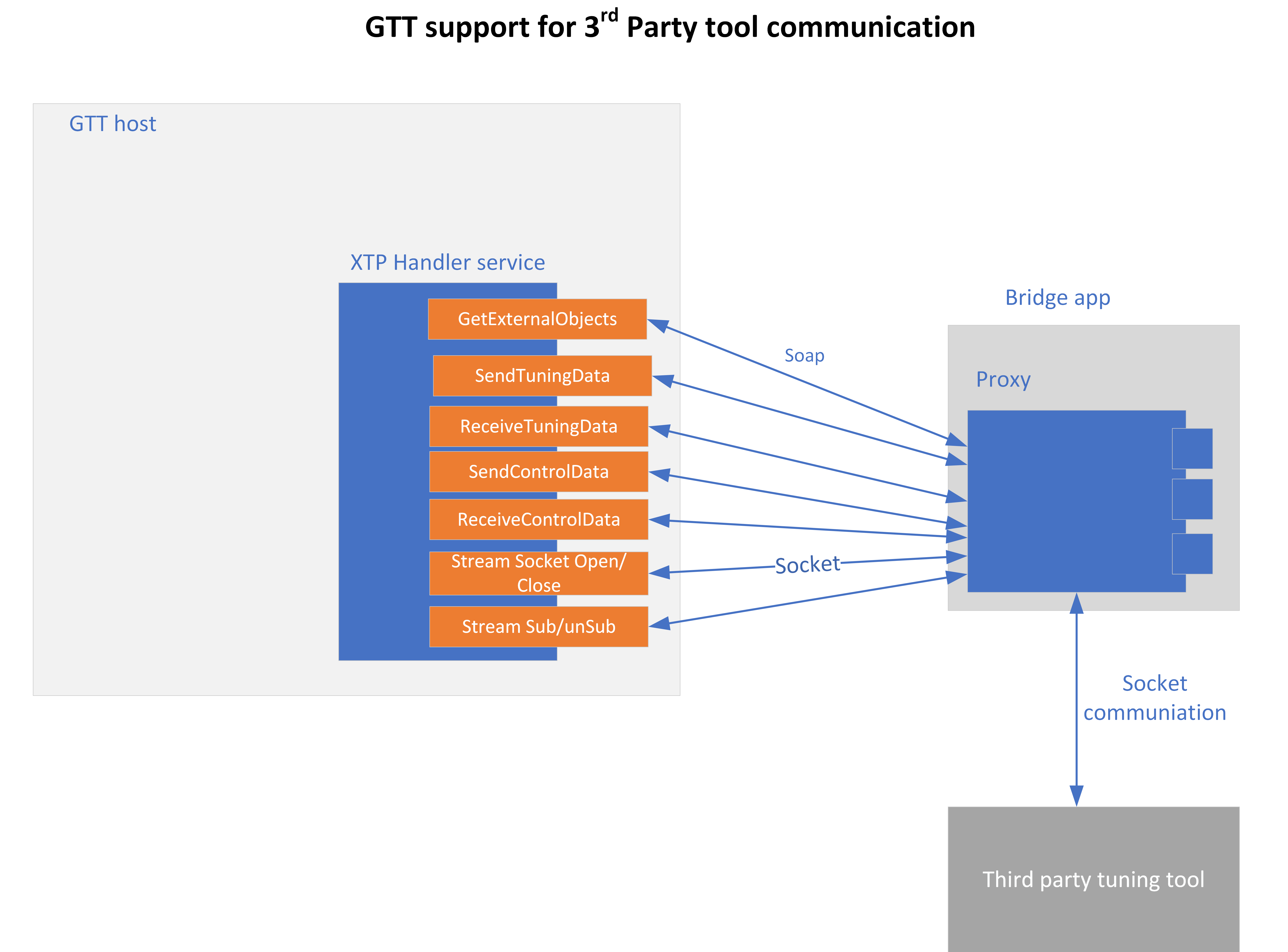
The requests from external tuning tools will come to GTT and GTT will forward these requests to the device. This is enabled through a WCF service endpoint that external tools can tap into.
To help external tools integrate with GTT, the GTT process hosts a WCF endpoint; external tools can connect to that endpoint and use the exposed APIs.
Refer the contact information mentioned in the latest release notes to get more details on “External third party tool” documentation and package.
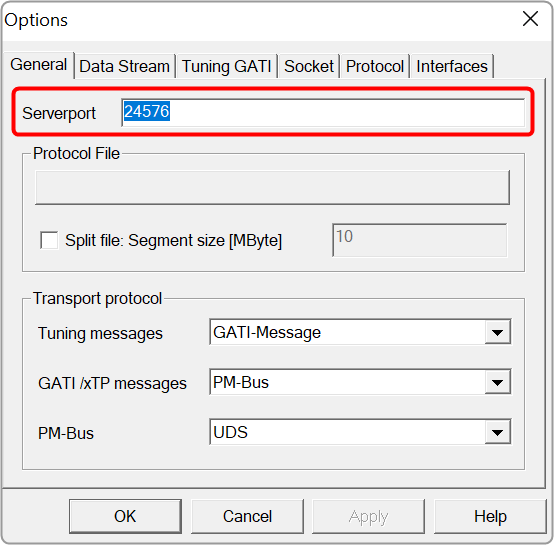
By default External Endpoints will use port 8080 for the communication.
Before proceeding with the following sections, it is understood that you have received 3 compressed zip files. It is recommended that you use these for integration purposes.
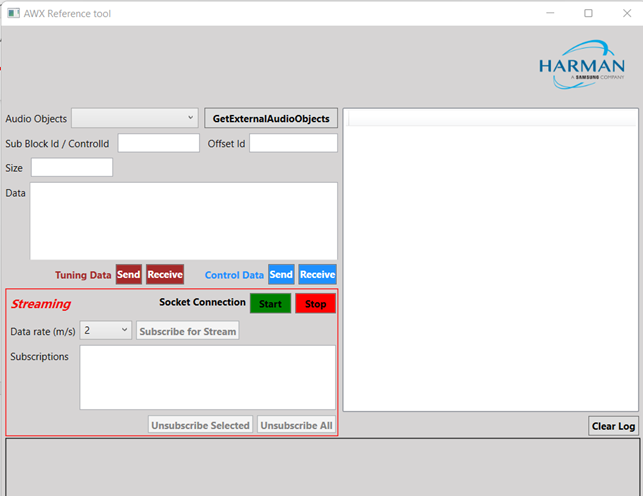
- HarmanReferenceTool.zip: This compressed folder contains an executable sample tool that you can run and verify the endpoint functionality. Unzip the HarmanReferenceTool.zip file, go to the HarmanReferenceToolReleasenet6.0-windows folder, and locate the ExternalTuningTool.exe. Run the exe to open Harman Reference Tool.
- ExternalToolCode.zip: This compressed folder contains visual studio solution for the sample tool. One can refer to this code to understand how the endpoint is accessed. Unzip the ExternalToolCode.zip file and locate the file under ExternalToolCodeExternalTool.
- WcfServiceProxyLib.zip: This compressed folder contains a proxy library dll that should be referenced for integration with the GTT endpoint.
The “WcfServiceProxy.dll” is a .net dll which has the implementation of the client code for the endpoint hosted in the GTT.
By default Third Party tuning tool will use port 8080 for the communication.
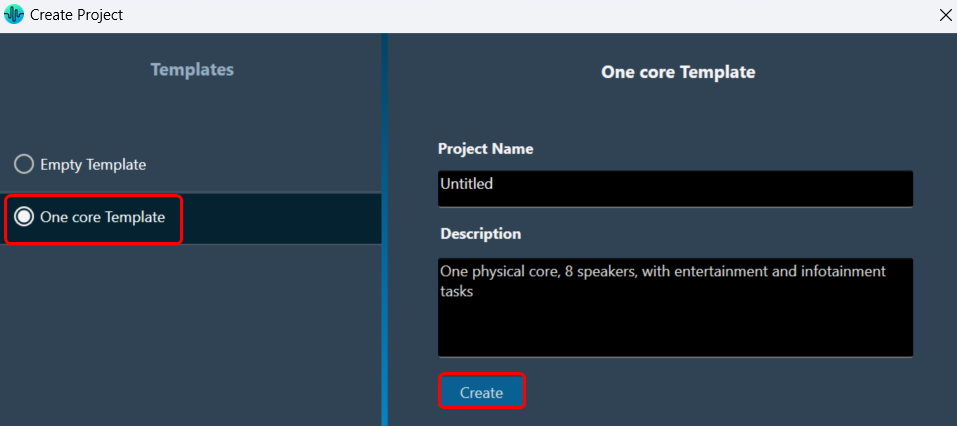
Setup
GTT needs a minimum setup for external endpoints to function.
- Right-click on GTT launcher and click on the “Run as administrator” option.
For the external endpoint feature to work correctly, it is necessary to run GTT as an administrator.
- GTT should have an open project. Only external audio objects can be accessed from external tools.
Accordingly, the project must contain at least one external audio object within the signal flow. An external audio object is defined as an object with Class ID between 9000 and 9999. - GTT should be connected to the device. The device can be a virtual device or a physical board.
- Click on the Start/Stop button to start the External Endpoint. The same button works as a toggle switch to start and stop the endpoint.
A license is required to use this feature. Contact the solution management team to enable the feature.
- Once the endpoint is hosted, the 3rd party applications can use the proxy dll or write their own proxy to access the WCF endpoint. For more details about WCF proxy, refer to “About WcfServiceProxy.dll in the GTT Third Party Tool Integration User Guide.
Supported Features
Sending and Receiving Tuning Data
To support sending and receiving tuning data, the following methods are exposed.
- GetExternalAudioObjects: This method will return all the 3rd party audio objects in the device.
- SendTuningDataAsync: This method is used to send tuning data to audio object.
- ReceiveTuningDataAsync: This method is used for receiving tuning data from an audio object.
Sending and Receiving Control Data
To support sending and receiving control data, the following methods are exposed.
- SendControlDataAsync: This method should be used to send control data by mentioning the control id and control data.
The control data supports 16.16 format.
- ReceiveControlDataAsync: This method can be used for retrieving control data by providing the control id to the control elements to be read back.
Streaming Methods
GTT also supports streaming with the following methods.
- EstablishSocketConnection: This method must be called first in order for streaming to work. The third-party tool should first establish a socket connection and then make a call to the port number where it is listening. GTT will connect to that port. This is a socket connection.
- DisconnectSocketConnection: This method is used to unsubscribe all the subscriptions and close the socket connection.
- SubscribeForStreamDataAsync: This method is used to subscribe for stream data for an audio object.
- UnSubscribeForStreamData: This method is used to stop or unsubscribes the stream data.
To know more about all the API methods described above, refer to the API Reference section in the GTT Third Party Tool Integration User Guide.
External Tool Interaction
The following are the steps to integrate with GTT.
By default GTT will host the WCF endpoint on this URL (http://localhost:8080/XtpHandlerService).
Steps to get started with the WCF service.
- Discover the service using this URL. Use the known tools like visual studio service reference tool or any 3rd party tools.
- Create a service reference for the same.
- Then using the service reference call the APIs for different operations.
Otherwise, developers can follow the “Third Party Tool Tuning Sequence Workflow” and “Third Party Tool Streaming Sequence Workflow” to write code to consume the endpoint hosted by GTT using the proxy library (WcfServiceProxy.dll) shared and explained in the GTT Third Party Tool Integration User Guide.
API References
GTT endpoint APIs definition and parameter details are provided in the GTT Third Party Tool Integration User Guide.
| API: ExternalAudioObject
API Function:
Description: This function will return all the audio objects that are used in the currently open signal flow in GTT. It returns only those audio objects which have Class ID between 9000 and 9999. Also, any audio objects that are listed in external category. |
| API: SendTuningDataAsync
API Function:
Description: This function will apply the data payload to the ExternalAudioObject passed into the function. |
| API: ReceiveTuningDataAsync
API Function:
Description: This function will retrieve tuning data from the ExternalAudioObject. |
| API: SendControlDataAsync
API Function:
Description: This function will send control data to the control id mentioned in the function. |
| API: ReceiveControlDataAsync
API Function:
Description: This function will get the control data from the control id that is passed into the function. |
| API: EstablishSocketConnection
API Function:
Description: This function will instruct GTT to connect to the socket connection listening at the port passed as parameter. The integrating application will create a socket connection and listen at a port and send this port id to GTT, so GTT can establish a connection and send stream data through the socket. |
| API: DisconnectSocketConnection
API Function:
Description: This function will instruct GTT to disconnect the previously established connection. The integrating application will close the socket connection. |
| API: SubscribeForStreamDataAsync
API Function:
Description: This function will create a subscription for data streaming of a particular state variable of the audio object mentioned at subblock/offset. This function can be used to subscribe for streaming of a particular data from audio object. Parameters include audio object, its subblock. There is an option to send the number of messages to be streamed per second and if the streaming data is to be retrieved before calc or after calc. All this needs to be supported by the audio object. Once the subscription is complete, the subscription id and status are returned to the object. |
| API: UnSubscribeForStreamData
API Function:
Description: This function will terminate the subscription that is currently running. GTT will stop the subscription that is started with the subscritionId passed as parameter. |
Use Cases and Workarounds
| Use Case | Workarounds |
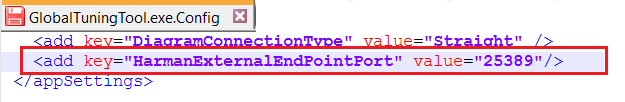
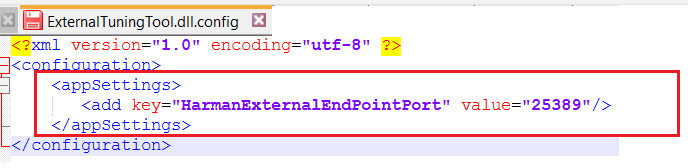
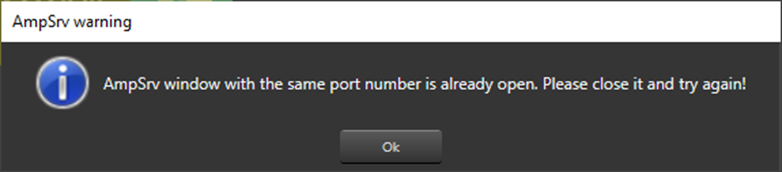
| Use Case 1: While starting External Endpoints from GTT, if you gets notification of port already being used. Then you need to perform configuration in GTT as well as in ExternalTuningTool. 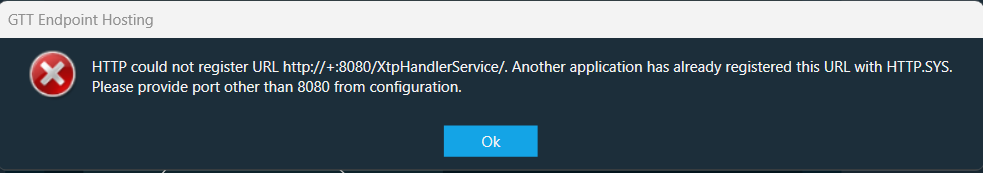 |
Close the GTT application and perform the below configurations:
By default the key does not exists in the config file. When configuring the config file, you need to add the key and the required port number. GTT configuration settings:
ExternalTuningTool configuration settings:
Key name must be ‘HarmanExternalEndPointPort’ and value must be same in GTT config as well as in ExternalTuningTool config. |